Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation is explained and the acceleration due to Earth’s gravity “g” is calculated. The concept of gravitational potential energy is examined and applied to the calculation of a planet’s escape velocity. These ideas are then extended to satellites in orbit and Kepler’s laws of planetary motion.
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Gravitation Near Earth’s Surface – Calculation of “g”
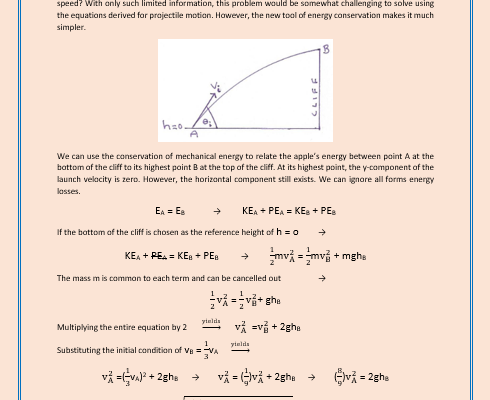
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Escape Velocity
- Satellites & Kepler’s Laws
- Practice Problems
Definitions of heat and temperature are introduced. Heat transfer through conduction, convection and radiation are studied, along with the ideas of specific heat as it applies to the laws of thermodynamics.
- Temperature
- Heat
- Heat Transfer
- Specific Heat Capacity & Method of Mixtures
- Latent Heat
- Laws of Thermodynamics
- Practice Problems
The propagation of energy through wave motion is analyzed. Concepts such as wave interference, oscillations, seismology, earthquakes, sound and the Doppler Effect are investigated.
- Longitudinal & Transverse Waves
- Interference
- Earthquakes
- Oscillations
- Sound
- The Doppler Effect
- Practice Problems
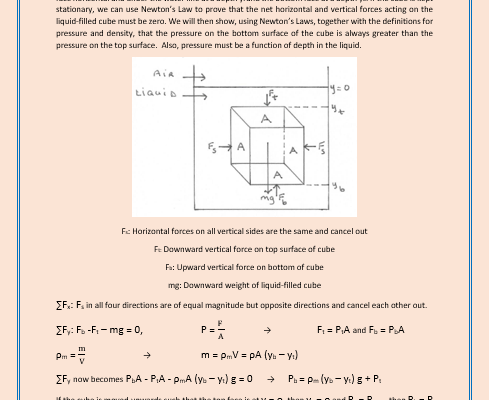
The equations of motion along with the mechanics of particles are applied to fluids. The definitions of pressure and density are explained and applied to principles such as Pascal, Archimedes and Bernoulli. The principle of flight and the equation of continuity are also studied.
- Pressure & Density
- Pressure vs. Depth
- Pressure vs. Altitude
- Density vs. Altitude
- Pascal’s Principle
- Archimedes’ Principle & Buoyancy
- Equation of Continuity
- Bernoulli’s Principle
- Viscosity
- Practice Problems
Systems of particles and rigid body rotation are considered with units of angular measurements. The equations of rotational motion are introduced and applied to the concepts of torque and angular momentum.
- Angular Measurement
- Angular Equations
- Kinetic Energy of Rotation
- Rotational Inertia
- Torque
- Angular Momentum
- Rolling
- Practice Problems
The conservation of linear momentum is introduced, along with the topics of center of mass and center of gravity. The equations of rocket motion are derived as an example of systems with varying mass in the framework of the conservation of linear momentum.
- Linear Momentum
- Conservation of Linear Momentum
- Center of Mass
- Rocket Motion
- Practice Problems
The concepts of energy, work done and power are considered. Their inter-relations are derived, along with the expression for the conservation of potential and kinetic energy through the work-kinetic energy theorem.
- Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem
- Power
- Potential Energy
- Conservation of Energy
- Practice Problems
The causes of motion are studied in the field of mechanics. Newton’s three laws of motion are investigated, then applied to systems of forces in multiple dimensions, including friction and drag forces.
- Force & Equilibrium 1D & 2D
- Friction
- Mechanics
- Uniform Circular Motion
- Practice Problems
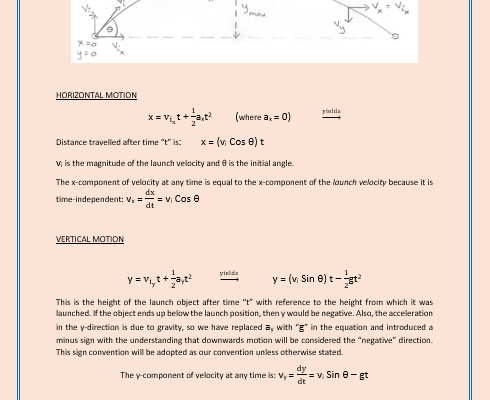
This is the study of kinematics. We derive the equations of motion from first principles, then apply them to the description of motion of everyday objects in both one and two dimensions, such as projectile motion.
- Vectors 2D & 3D
- Equations of Motion
- Kinematics
- Projectile Motion
- Practice Problems